CT Scan Services: Advanced 3D Diagnostic Imaging
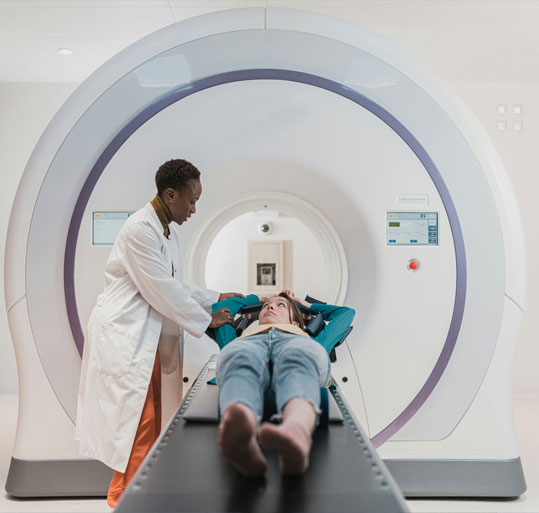
What is a CT Scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) Scan is a fast, painless imaging test that combines X-rays with computer technology to create:
✔ Cross-sectional 3D images of bones, organs, and blood vessels
✔ Detailed views of the brain, chest, abdomen, and spine
It provides more comprehensive data than standard X-rays for accurate diagnosis of:
- Trauma injuries (internal bleeding, fractures)
- Tumors & cancers
- Heart/lung diseases
- Complex infections
How Does a CT Scan Work?
1. Preparation
- Fasting 4–6 hours (for contrast-enhanced scans)
- Wear loose clothing, remove metal objects
- Contrast dye may be injected/oral (iodine or barium)
2. During the Scan (10–30 mins)
- Lie on a motorized table that slides into a donut-shaped scanner
- Stay still while the machine rotates, capturing sliced images (0.5mm precision)
- Painless – Only requires brief breath-holds
3. After the Scan
- Radiologist analyzes images within 24–48 hours (sooner for emergencies)
- No recovery needed – Drink water to flush out contrast dye
Why Dr. Solanki Recommends It
![]()
Unmatched Precision
Detects tumors as small as 1mm (vs. X-ray’s 5mm limit) and Guides biopsies, surgeries, and radiation therapy
![]()
Speed & Efficiency
5x faster than MRI – Critical for stroke/trauma cases and Whole-body scans in <5 minutes
![]()
Safer than Ever
Low-dose radiation protocols (up to 50% less than traditional CT) and Non-ionic contrast dyes reduce allergy risks
Sample Results Timeline
| Condition | CT Findings | Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Lung Cancer | Irregular mass, spiculated edges | Biopsy + PET scan |
| Brain Hemorrhage | Bright white blood collection | Emergency neurosurgery |
| Kidney Stones | High-density stones in ureter | Lithotripsy/medication |
| Appendicitis | Inflamed appendix, fluid | Laparoscopic surgery |
FAQs : Your Questions Answered
1. Is a CT scan safe during pregnancy?
Avoid unless critical (radiation risk to fetus). MRI preferred
2. CT vs. MRI – Which is better?
| CT Scan | MRI |
|---|---|
| Faster (minutes) | Slower (30–60 mins) |
| Better for bones/bleeding | Superior for soft tissues |
| Uses radiation | Radiation-free |
3. Why is contrast dye used?
- Highlights blood vessels, tumors, inflammation (e.g., in strokes).
- Side effects (rare): Warm flush, metallic taste, mild nausea.
4. How much radiation is in a CT scan?
- Chest CT ≈ 70 X-rays (but still within safe annual limits).
- Low-dose protocols minimize exposure.
5. What’s the cost in India?
- ₹3,000–12,000 (varies by body part/contrast use).
- Insurance-covered for most diagnoses.

